MySQL CREATE TABLE Statement

The CREATE TABLE statement is used to create a new table in a database.
Syntax
CREATE TABLE table_name (
column1 datatype,
column2 datatype,
column3 datatype,
....
);The column parameters specify the names of the columns of the table.
The datatype parameter specifies the type of data the column can hold (e.g. varchar, integer, date, etc.).
MySQL CREATE TABLE Example
The following example creates a table called “Customers” that contains five columns: CustomerID, CustomerName, ContactName, and Country:
Example
CREATE TABLE Customers (
CustomerID int,
CustomerName varchar(255),
ContactName int(10),
Country varchar(255)
);The CustomerID column is of type int and will hold an integer.
The CustomerName, ContactName, and Country columns are of type varchar and will hold characters, and the maximum length for these fields is 255 characters.
MySQL INSERT INTO TABLE Example
The following SQL statement inserts a new record in the “Customers” table:
Example
INSERT INTO Customers (CustomerID, CustomerName, ContactName, Country)
VALUES (1, 'Alfreds Futterkiste', 'Maria Anders', 'Germany');By using the above step we can insert more data into it and after the data insertion table looks like as shown below:
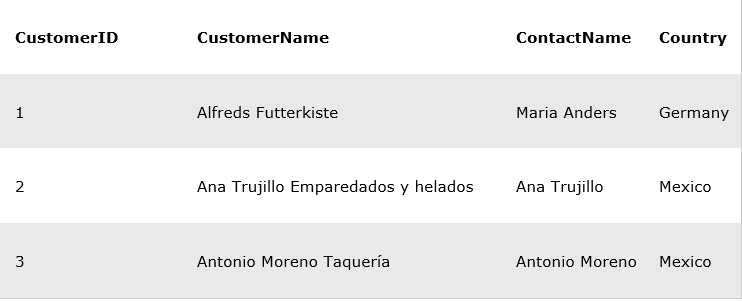
And if you want to gain more knowledge on the topic insert into you can learn here https://medium.com/@bhavithach8/mysql-insert-into-statement-8cdc0670681a
Create Table Using Another Table
A copy of an existing table can also be created using CREATE TABLE.
The new table gets the same column definitions. All columns or specific columns can be selected.
If you create a new table using an existing table, the new table will be filled with the existing values from the old table.
Syntax
CREATE TABLE new_table_name AS
SELECT column1, column2,...
FROM existing_table_name
WHERE ....;The following SQL creates a new table called “DuplicateTables” (which is a copy of the “Customers” table):
Example
CREATE TABLE DuplicateTable As
SELECT customername, contactname
FROM customers;