MySQL UNION Operator

The UNION operator is used to combine the result-set of two or more SELECT statements.
- Every SELECT statement within UNION must have the same number of columns
- The columns must also have similar data types
- The columns in every SELECT statement must also be in the same order
UNION Syntax
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1
UNION
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table2;UNION ALL Syntax
The UNIONoperator selects only distinct values by default. To allow duplicate values, use UNION ALL :
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1
UNION ALL
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table2;Demo Database
In this tutorial we will use the well-known Northwind sample database.
Below is a selection from the “Customers” table:
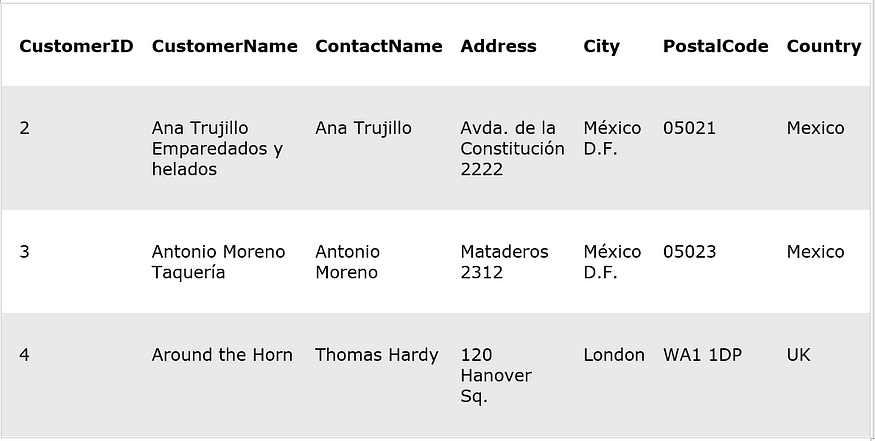
And a selection from the “Suppliers” table:

SQL UNION Example
The following SQL statement returns the cities (only distinct values) from both the “Customers” and the “Suppliers” table:
Example
SELECT City FROM Customers
UNION
SELECT City FROM Suppliers
ORDER BY City;SQL UNION ALL Example
The following SQL statement returns the cities (duplicate values also) from both the “Customers” and the “Suppliers” table:
Example
SELECT City FROM Customers
UNION ALL
SELECT City FROM Suppliers
ORDER BY City;SQL UNION With WHERE
The following SQL statement returns the German cities (only distinct values) from both the “Customers” and the “Suppliers” table:
Example
SELECT City, Country FROM Customers
WHERE Country='Germany'
UNION
SELECT City, Country FROM Suppliers
WHERE Country='Germany'
ORDER BY City;Another UNION Example
The following SQL statement lists all customers and suppliers:
Example
SELECT 'Customer' AS Type, ContactName, City, Country
FROM Customers
UNION
SELECT 'Supplier', ContactName, City, Country
FROM Suppliers;

No comments:
Post a Comment