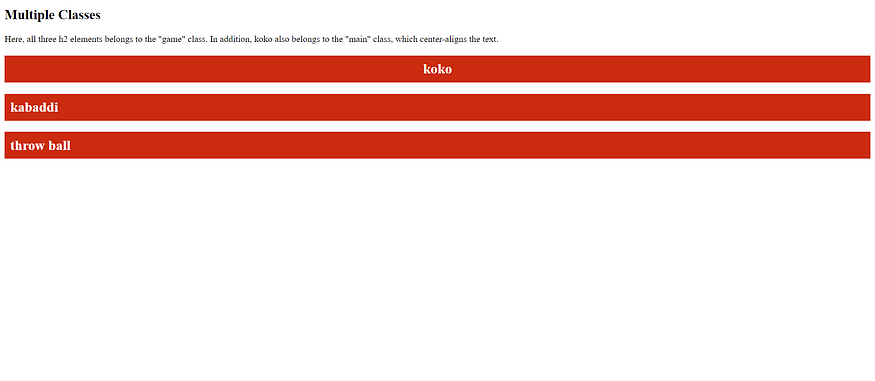
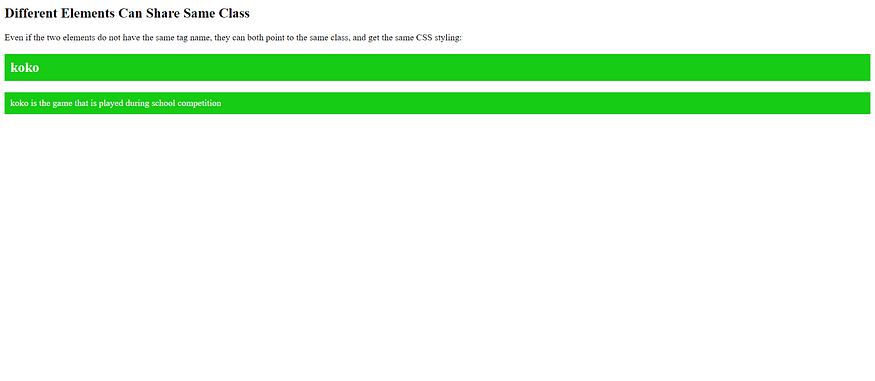
The HTML meta Element

The <meta> element is typically used to specify the character set, page description, keywords, author of the document, and viewport settings.
The metadata will not be displayed on the page, but is used by browsers (how to display content or reload page), by search engines (keywords), and other web services.
Examples
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="description" content="Free Web tutorials">
<meta name="keywords" content="HTML, CSS, JavaScript">
<meta name="author" content="John Doe">
</head>
<body>
<p>All meta information goes inside the head section.</p>
</body>
Setting The Viewport
The viewport is the user’s visible area of a web page. It varies with the device — it will be smaller on a mobile phone than on a computer screen.
You should include the following <meta> element in all your web pages:
This gives the browser instructions on how to control the page’s dimensions and scaling.
The width=device-width part sets the width of the page to follow the screen-width of the device (which will vary depending on the device).
The initial-scale=0.1 part sets the initial zoom level when the page is first loaded by the browser.
Here is an example of a web page without the viewport meta tag, and the same web page with the viewport meta tag: