MySQL INSERT INTO
Statement

The INSERT INTO statement is used to insert new records in a table.
INSERT INTO Syntax
It is possible to write the INSERT INTO statement in two ways:
- Specify both the column names and the values to be inserted:
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, column3, ...)
VALUES (value1, value2, value3, ...);2. If you are adding values for all the columns of the table, you do not need to specify the column names in the SQL query. However, make sure the order of the values is in the same order as the columns in the table. Here, the INSER INTO syntax would be as follows:
INSERT INTO table_name
VALUES (value1, value2, value3, ...);Demo Database
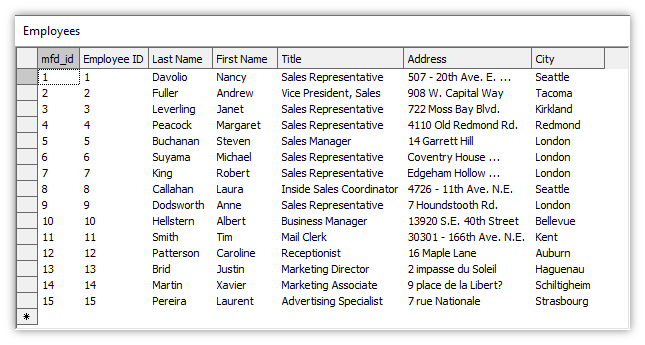
Below is a selection from the “Employees” table in the sample database:
INSERT INTO Example
The following SQL statement inserts a new record in the “Employees” table:
Example
INSERT INTO Employees(LastName, FirstName, Title, Address, City)
VALUES ('Harry', 'singh', 'Business Manager', '7 rue Nationale', 'Strasbourg');Did you notice that we did not insert any number into the EmployeeID field?
The EmployeeID column is an auto_increment field and will be generated automatically when a new record is inserted into the table.
Insert Data Only in Specified Columns
It is also possible to only insert data in specific columns.
The following SQL statement will insert a new record, but only insert data in the “LastName”, “City”, columns (EmployeeID will be updated automatically):
Example
INSERT INTO Employees(LastName, City)
VALUES ('Andrew', 'London');
No comments:
Post a Comment